Today, I want to delve deeper into the practical applications of semantic communications, examine the challenges we face in implementation, and outline what I believe is the most effective path forward.
Let’s begin by exploring the transformative potential of semantic communication across various domains.
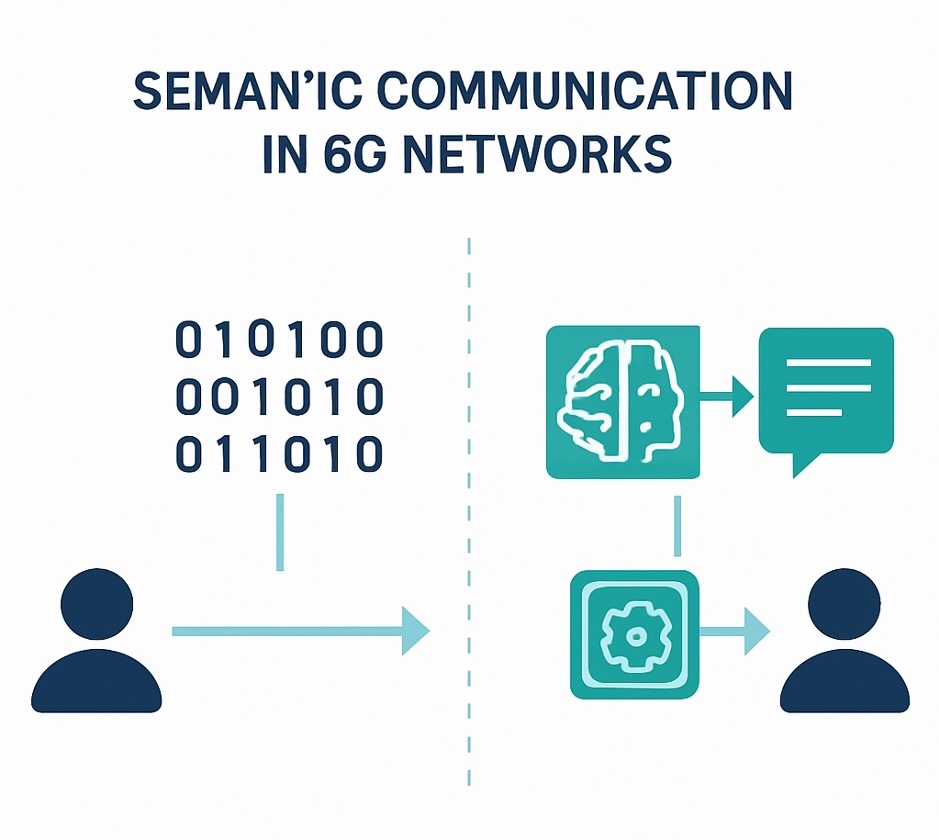
In the realm of 6G and beyond, semantic communication will enable significantly leaner, context-aware data exchange for ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC). This isn’t merely an incremental improvement; it represents a fundamental shift in how we approach network efficiency and reliability.
For Machine-to-Machine (M2M) and IoT applications, the implications are particularly profound. Devices will be able to understand intent without requiring verbose data transmission, resulting in substantial savings in both spectrum usage and energy consumption. In a world moving toward billions of connected devices, this efficiency gain becomes not just beneficial but necessary.
Autonomous systems present another compelling use case. When vehicles and robots can communicate purpose rather than raw data, we see marked improvements in decision-making speed and safety. This shift from data-centric to meaning-centric communication could be the difference between an autonomous vehicle stopping in time or not.
The future of immersive experiences, including extended reality, holographic communication, and digital humans, will increasingly rely on shared context and compressed meaning. These applications demand not just bandwidth but intelligent use of that bandwidth, making semantic communication an ideal approach.
Finally, Digital Twins and Cognitive Networks will benefit tremendously from real-time mirroring and network self-awareness based on semantics rather than full datasets. This allows for more sophisticated modelling and prediction with less overhead.
Despite these promising applications, several significant challenges stand in our way.
Perhaps the most fundamental is what I call “semantic noise” errors in understanding, not just in transmission. This represents an entirely new category of “noise” in the communication channel that our traditional models aren’t equipped to address.
Context synchronization presents another hurdle. How do we ensure that sender and receiver share enough background knowledge to interpret messages correctly? Without this shared foundation, semantic communication breaks down.
From a theoretical perspective, modelling meaning mathematically remains a complex challenge. We need to move beyond bits to quantify and encode “meaning” in ways that are both efficient and reliable.
The dependence on advanced AI also presents practical challenges. Semantic communication requires deep integration with natural language processing, reasoning models, and adaptive learning technologies that are still evolving rapidly.
Finally, standardization poses a significant obstacle. Our current network protocols simply weren’t built for semantic intent exchange, requiring substantial rethinking of our fundamental approaches.
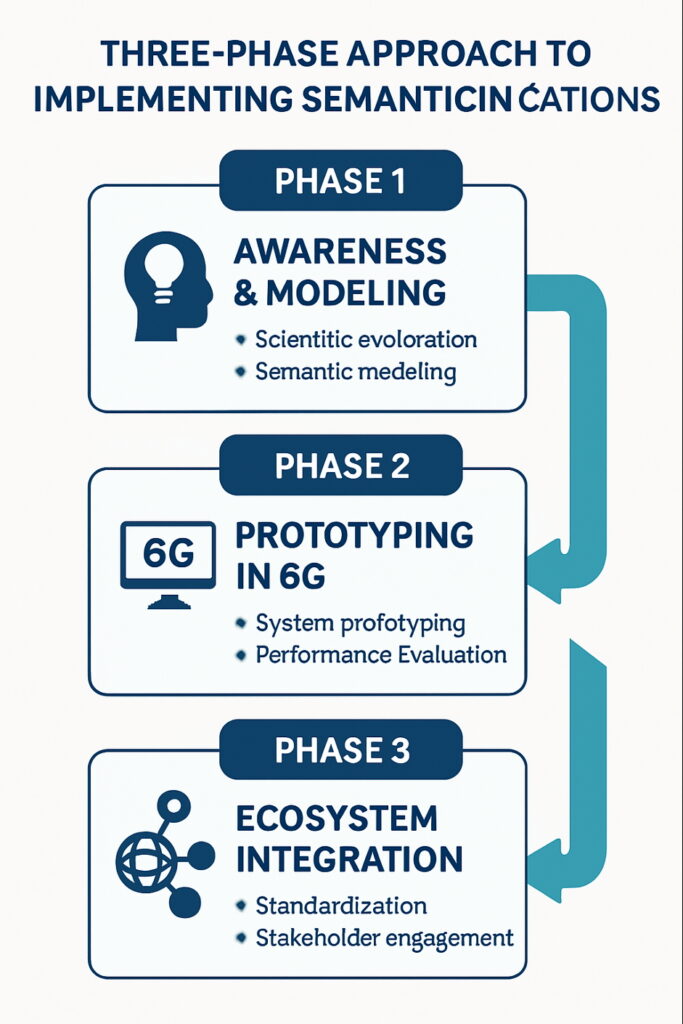
In the first phase, Awareness & Modelling, we need to define semantic entropy, capacity, and metrics while developing proof-of-concept systems in research settings. This foundational work should include embedding semantic layers into AI-enhanced protocols, establishing the technical groundwork for what follows.
The second phase, Prototyping in 6G Environments, involves integrating semantic communication with URLLC and mMTC (massive Machine Type Communications). We should test these integrations with Digital Twin networks and edge AI, while simultaneously establishing pre-standardization working groups to ensure alignment across the industry.
The final phase, Ecosystem Integration & Commercialization, will require embedding semantic modules into chipsets and network functions, deploying them in smart cities, Industry 4.0 environments, and immersive media applications. Standardization through bodies like 3GPP and ITU will be crucial during this phase to ensure global interoperability.
This journey toward semantic communication isn’t just a technical evolution; it’s a reimagining of how networks understand and transmit meaning. The challenges are substantial, but the potential rewards in efficiency, intelligence, and new capabilities make this one of the most exciting frontiers in telecommunications.
This blog post was written by Amr Ashraf, Product Architect and Support Director at Digis Squared.