Introduction
As mobile networks continue to evolve with 5G, ensuring optimal indoor connectivity is more critical than ever. INOS (Indoor Network Optimization Solution) is redefining how operators and engineers approach indoor testing with its advanced tools, robust features, and a newly upgraded Indoor Kit. Designed to tackle the unique challenges of indoor environments, the INOS Indoor Kit offers significant improvements in software, hardware, and overall functionality to deliver superior usability, reliability, and results.
The Importance of Indoor Testing
Indoor spaces like malls, airports, and office buildings pose unique challenges for network optimization due to:
- Architectural complexity: Thick walls and multiple floors impede signal propagation.
- User density: Crowded environments generate high network demand.
- Interference: Co-channel interference can degrade signal quality.
These challenges make precise and efficient indoor network testing crucial for delivering seamless connectivity.
Enhancements in the INOS Indoor Kit
Software Improvements (Icons)
- Revamped User Interface (UI):
The new UI offers an intuitive design for enhanced accessibility, streamlining control, and monitoring processes for users. - Enhanced Connectivity Options:
Supporting Internet, WLAN, and Bluetooth connections, the kit provides robust and flexible inter-device connectivity. - Comprehensive Control Capabilities:
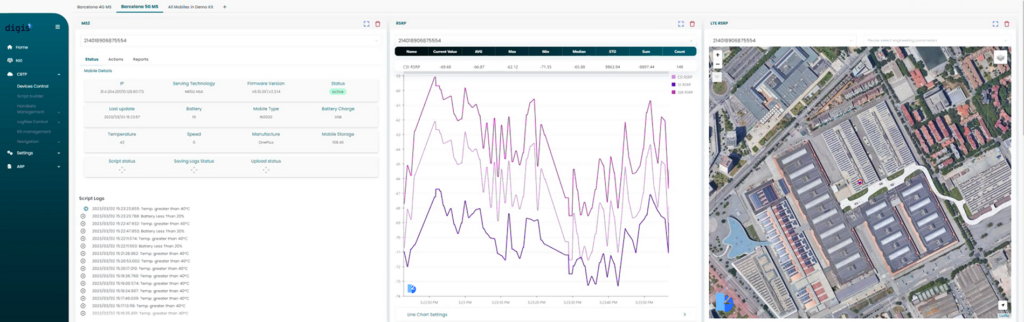
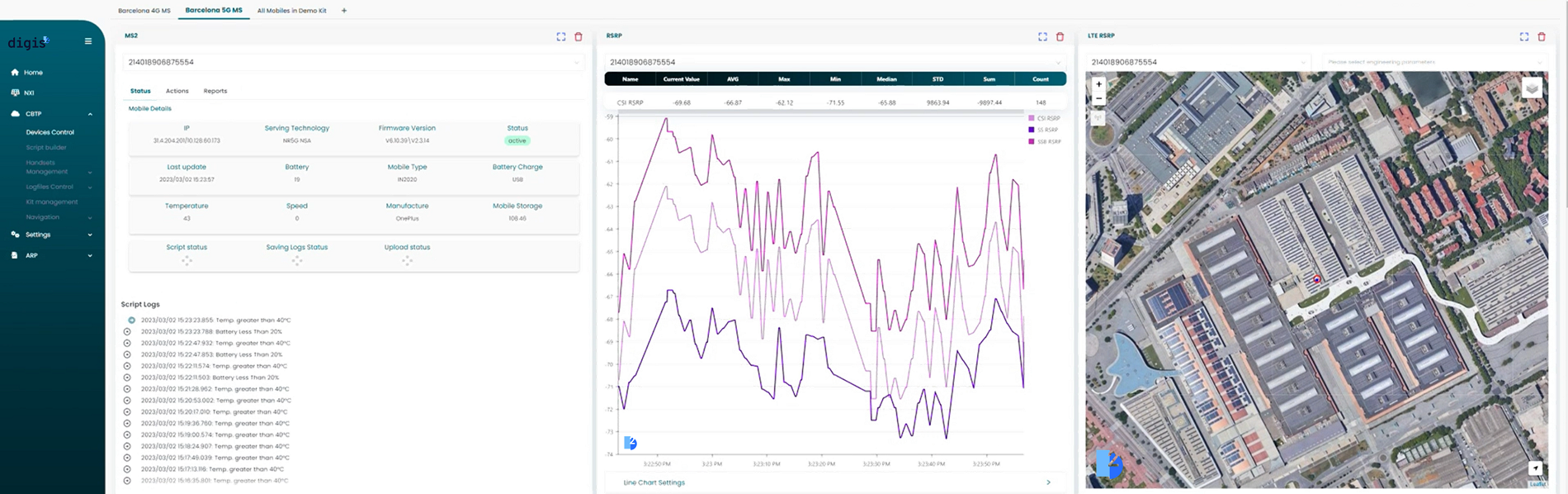
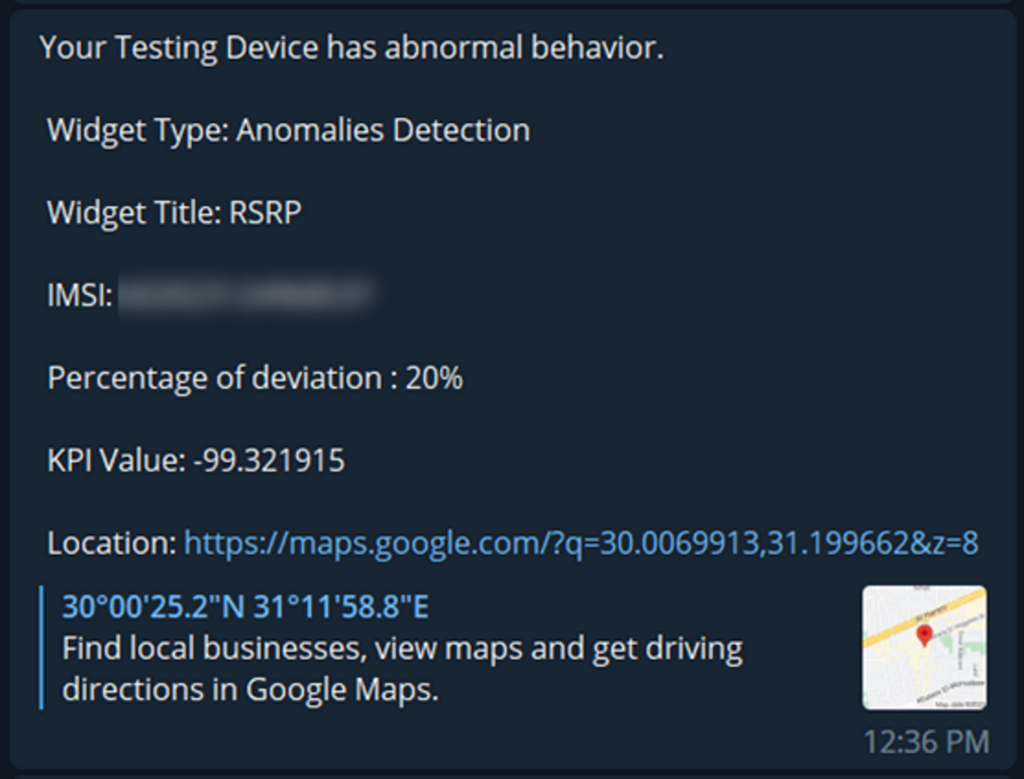
The tablet serves as a central hub, allowing users to control every connected device and monitor KPIs directly. - Centralized Alarm Notifications:
Alarm notifications from all connected devices are displayed on the tablet in real-time, enabling prompt troubleshooting.
Hardware Upgrades
- Ergonomic and Lightweight Design:
A portable, lighter design ensures ease of use in various indoor scenarios. - Extended Battery Life:
Powering up to 12 devices for 8 hours of continuous operation, the kit supports long-duration tasks without frequent recharging. - Smart Cooling System:
An intelligent cooling mechanism activates based on system temperature, ensuring consistent performance without overheating.
Key Features and Differentiators
The INOS Indoor Kit offers several standout features that set it apart from competitors:
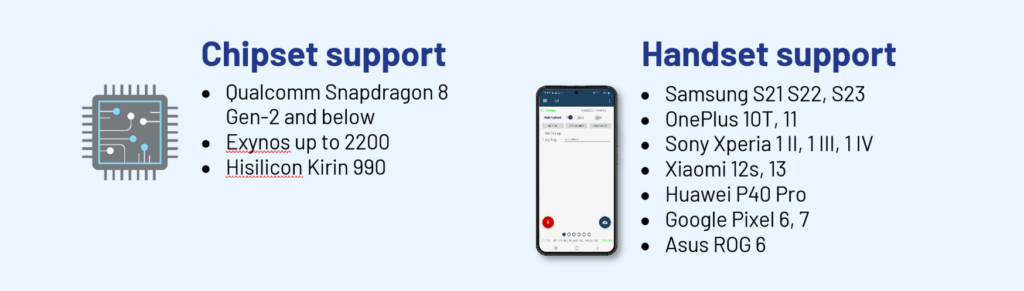
- 5G Support Across All Devices:
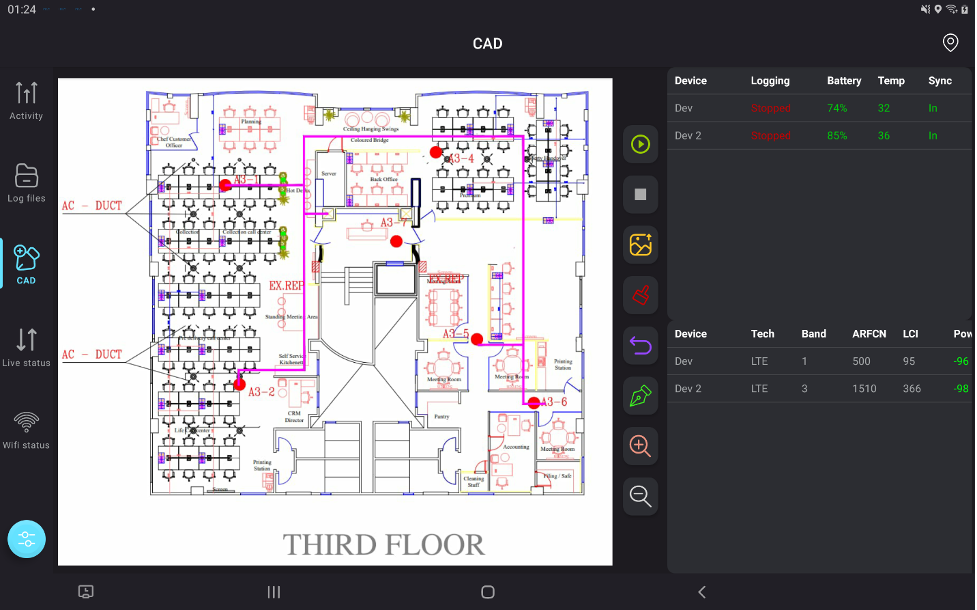
Fully optimized for 5G testing, supporting all devices within the kit to handle the latest network demands. - Tablet as a Centralized Display:
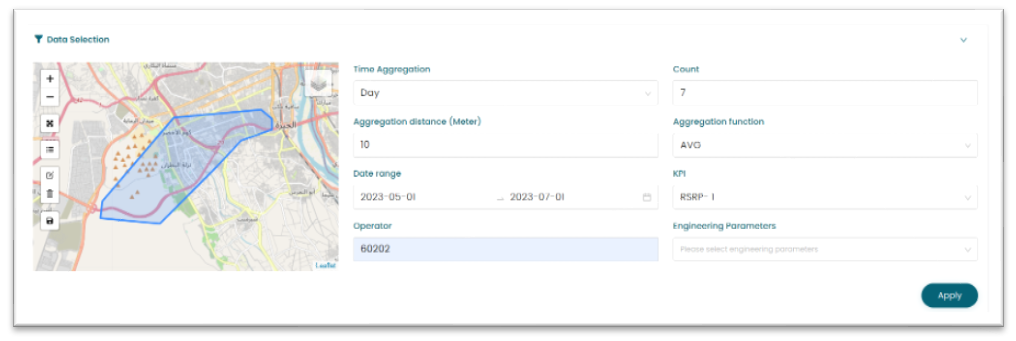
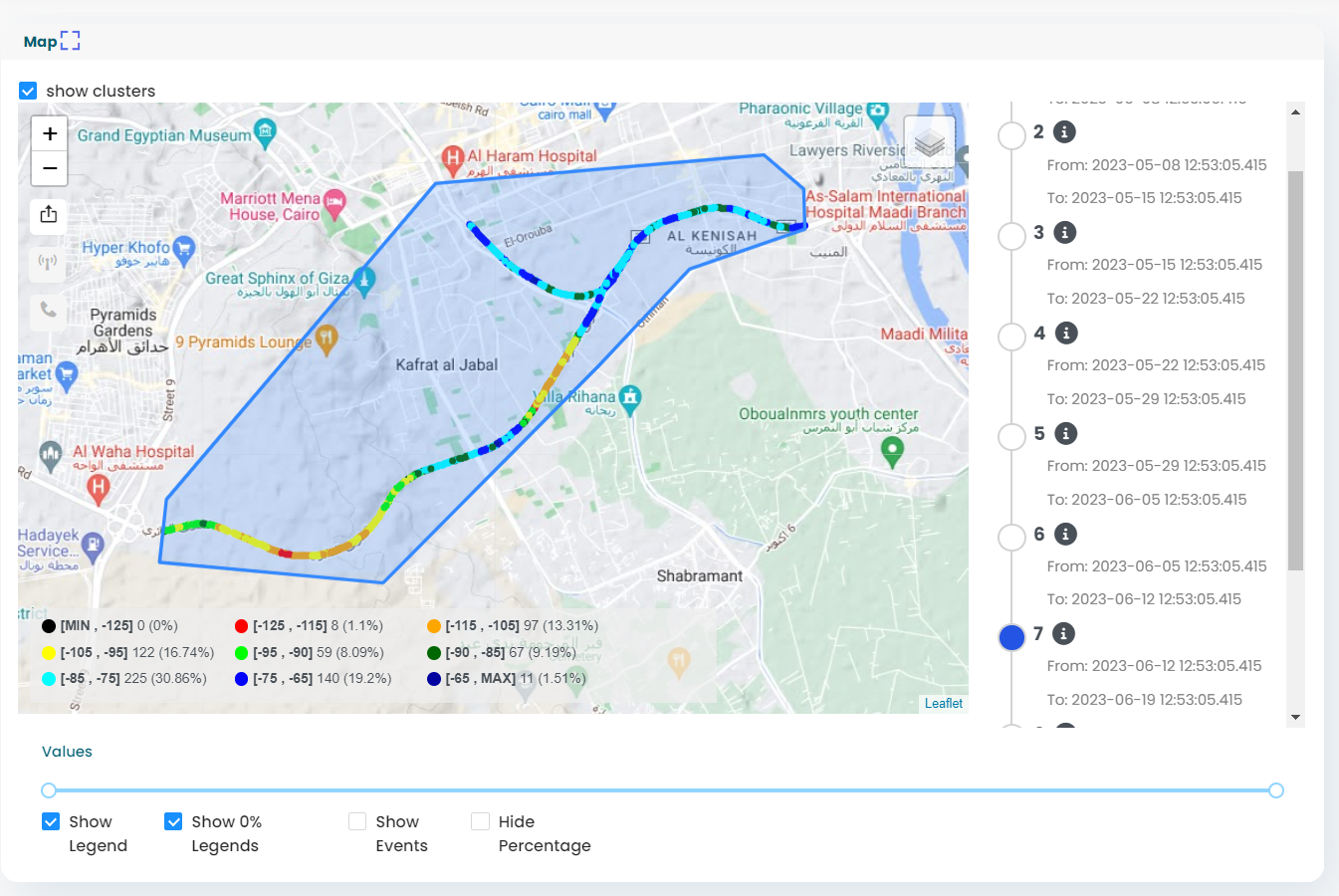
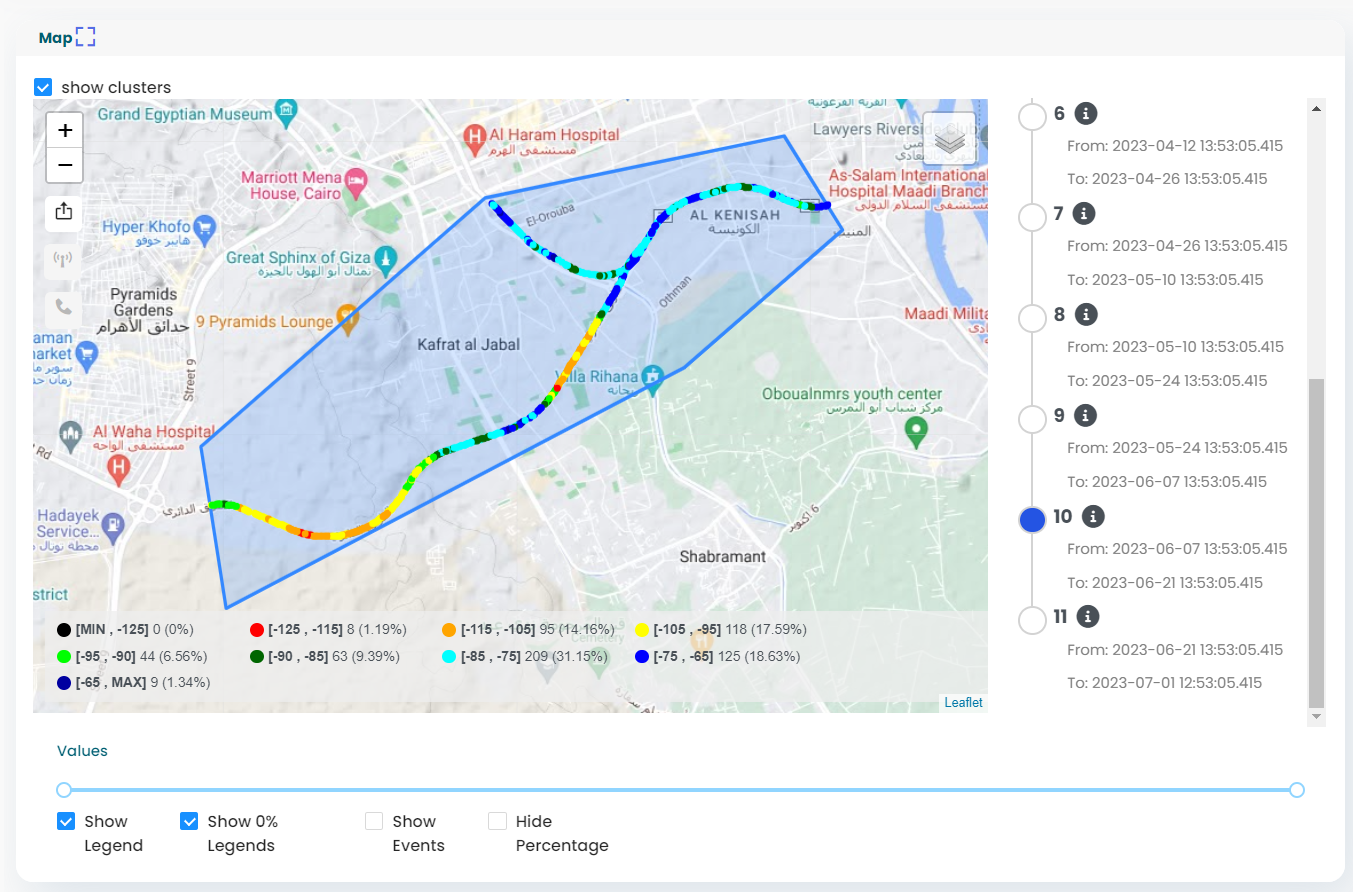
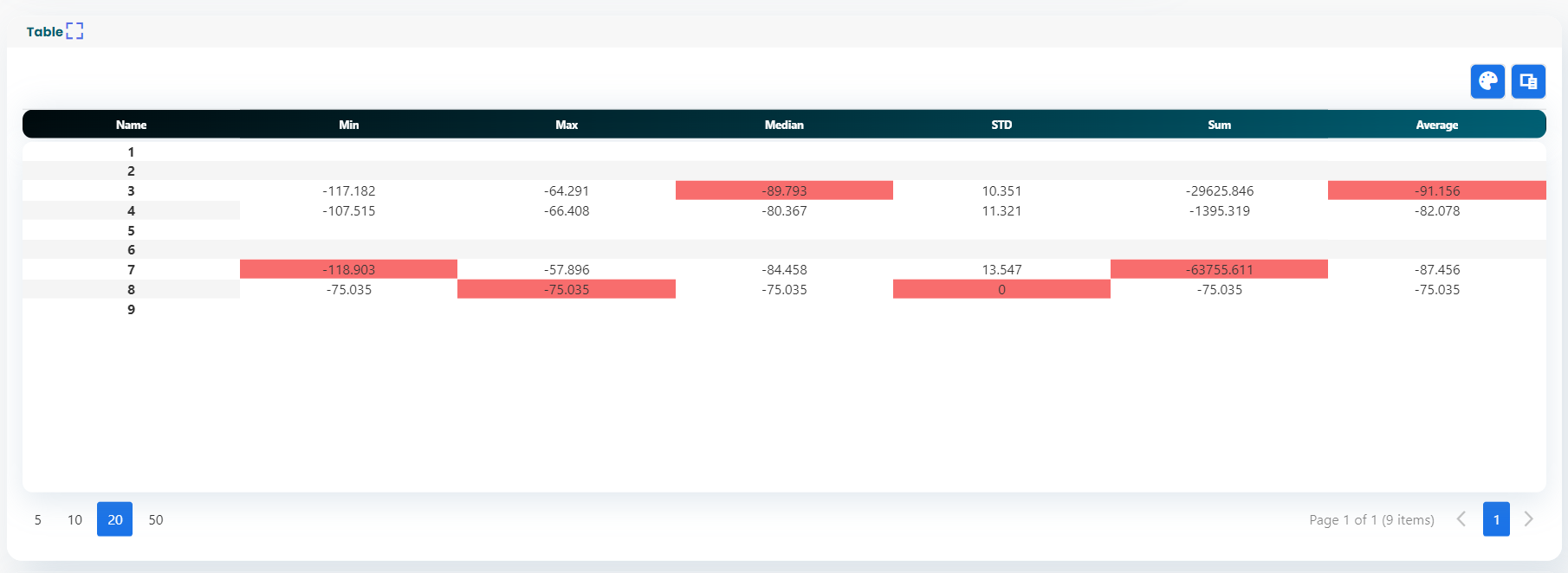
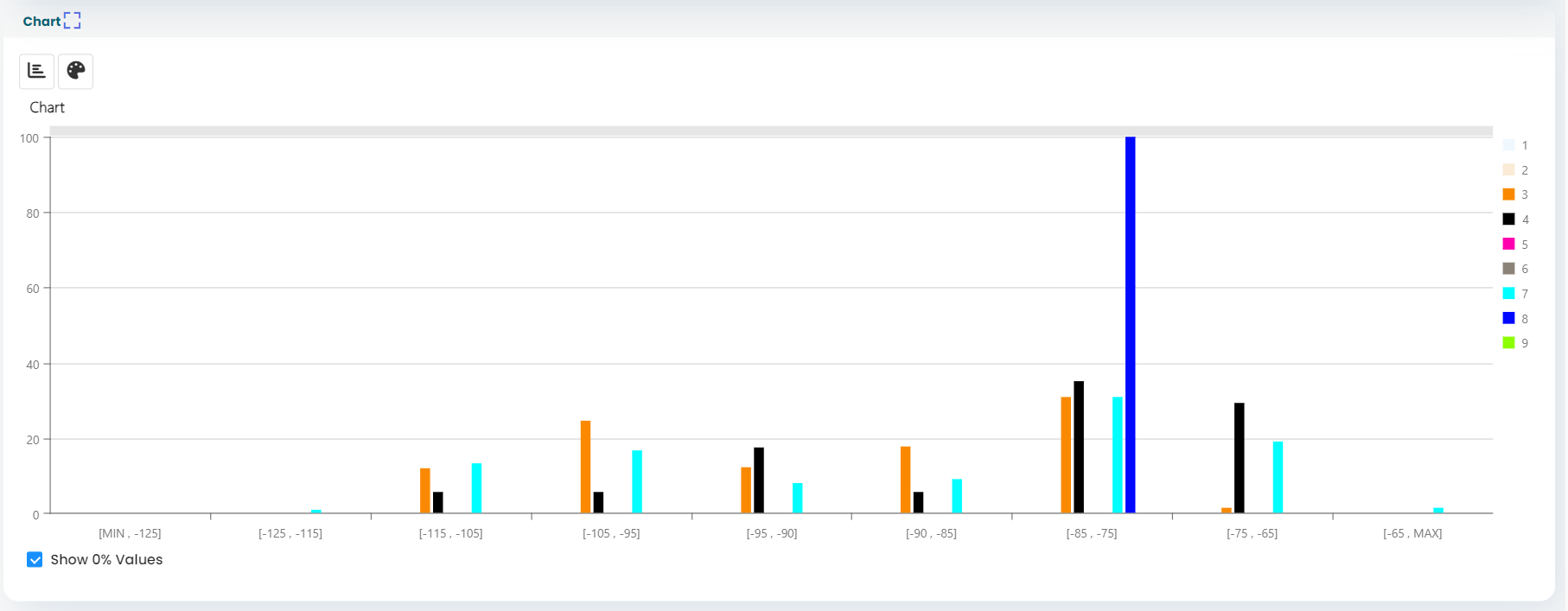
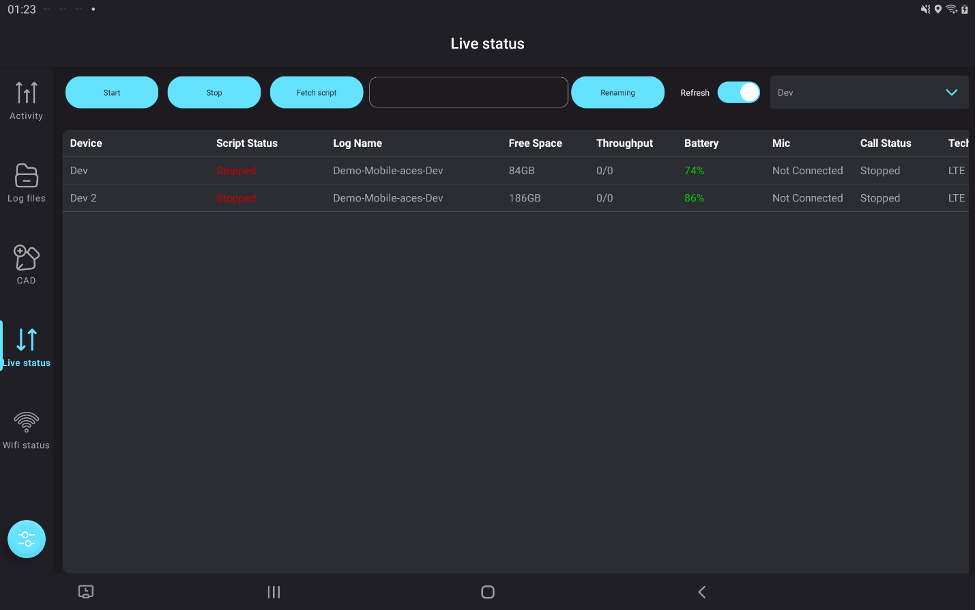
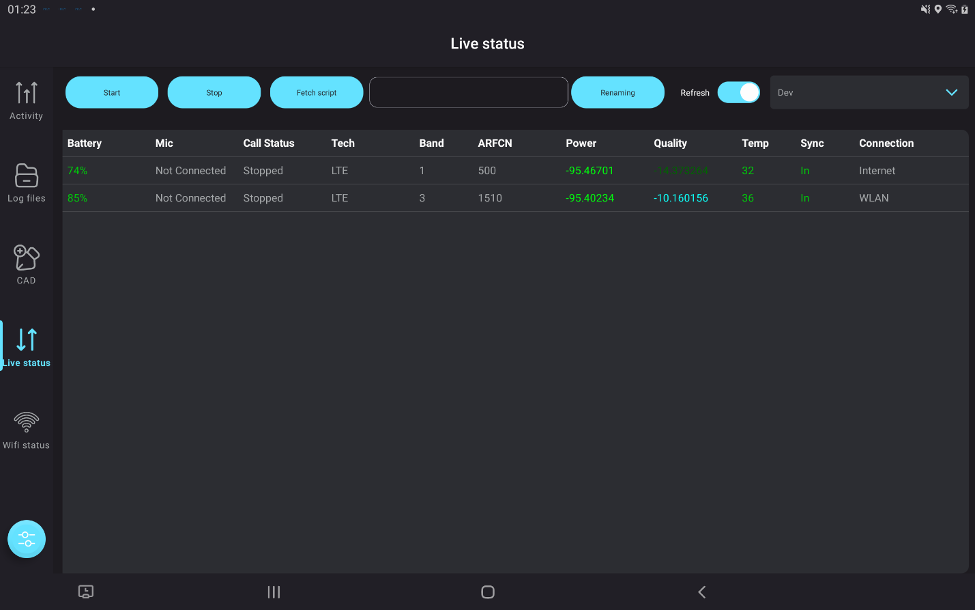
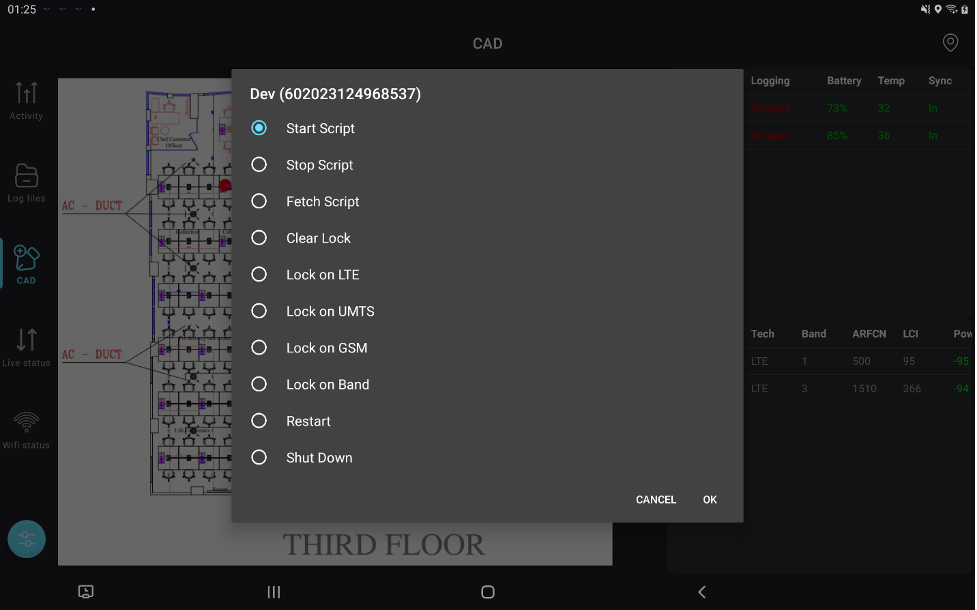
Displays real-time radio KPIs, with intuitive visualizations and insights for quick decision-making. - Advanced Device Management via Tablet:
- Control multiple phones directly.
- Color-coded indicators highlight synced devices, poor KPIs, and ongoing logfile recordings, allowing users to focus on critical areas.
- Support for Large Layout Images:
Unlike competitors, INOS excels at handling and displaying large indoor layouts, ensuring no testing area is overlooked. - Automated Processes:
- Logfile Uploading and Collection: Eliminates manual intervention, saving time and effort.
- Post-Processing Automation: Simplifies report generation and routine tasks that traditionally require manual copy-paste workflows.
- Comprehensive Support Model:
INOS provides end-to-end support for all product aspects, ensuring users have the help they need at every stage. - Expandable Kit Design:
Offers the flexibility to add more devices, making it adaptable to different indoor testing scales. - Enhanced Connectivity:
INOS leverages Internet, WLAN, and Bluetooth for device control, overcoming the limitations of competitors who rely solely on Bluetooth (limited to 8 devices and prone to connectivity issues).
Why INOS Stands Out in Indoor Testing
INOS combines cutting-edge technology with user-centric design to deliver a superior indoor testing experience. With its latest enhancements, it ensures that telecom operators and network engineers have the tools they need to achieve:
- Unmatched Accuracy: Collect and analyze data with precision.
- Greater Efficiency: Streamlined workflows and automation save time and effort.
- Enhanced Portability: Lightweight design and extended battery life make it perfect for demanding indoor environments.
Conclusion
The INOS Indoor Kit, with its latest software and hardware upgrades, is a game-changer for indoor network optimization. By focusing on usability, functionality, and reliability, it empowers operators to tackle even the most challenging scenarios with confidence.
Ready to elevate your indoor testing? Discover how the enhanced INOS Indoor Kit can revolutionize your network optimization strategy.
This blog post was written by Amr Ashraf, Product Architect and Support Director at Digis Squared. With extensive experience in telecom solutions and AI-driven technologies, Amr plays a key role in developing and optimizing our innovative products to enhance network performance and operational efficiency.