Reflections in 2025: Progress and Transformation at Digis Squared

As we approach the end of the year, it is worth pausing to reflect on the significant technological shifts that have characterized 2025. At Digis Squared, our focus has been not only on innovation, but also on achieving measurable progress in addressing the ongoing challenges faced by Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and the telecommunications sector. This year has marked a turning point, where the concept of intelligent networks has begun to materialise in practical operations. This transformation has been fuelled by the urgent need to manage increasingly complex systems, respond to mounting cost pressures, and navigate a rapidly changing threat environment.
Operational Consolidation and Application
In my role as Chief Technology Officer, I have witnessed 2025 becoming the year of consolidation and practical application. Our collective efforts have moved beyond the initial excitement surrounding emerging technologies such as generative AI. Instead, we have dedicated ourselves to the tangible development of networks that are capable of self-awareness and self-optimisation. The momentum established through the deployment of our solutions and the insights gained from real-world implementations now positions us strongly for an even more dynamic year ahead in 2026.
Looking Back and Ahead: Addressing Core Challenges and Future Trends
This review aims to summarize the fundamental challenges currently facing the telecoms industry, to highlight the ways in which our technologies are directly tackling these issues, and to share my perspective on the trends that are likely to shape the future of our sector.
The Complexity Crisis in Modern Telecom Networks
The modern telecommunications network presents a formidable challenge for operators due to its intricate composition. These networks are built from a vast array of equipment sourced from multiple vendors, layered with technologies that span generations—from 2G through to 5G—and encompass a diverse range of domains such as Radio Access Networks (RAN), Core networks, Transport, Business Support Systems (BSS), and IP Multimedia Subsystems (IMS).
This inherent complexity has evolved into a significant crisis for Mobile Network Operators (MNOs). The interplay of different vendors and technologies, combined with the multifaceted nature of network operations, has resulted in a landscape where operational efficiency is frequently compromised. Critical challenges have emerged; each demanding the implementation of cognitive solutions to restore control, streamline processes, and ensure the ongoing viability and security of telecom operations.
| Challenge Area | Description | Impact |
| Operational Inefficiency | Sheer volume of alarms and data makes root cause analysis slow and manual. | Long Mean Time To Resolution (MTTR) and high operational expenditure (OPEX)1. |
| Budget Constraints | Pressure to reduce OPEX while simultaneously investing in 5G, 6G R&D, and network modernization. | Need for highly efficient, automated tools that minimize human intervention. |
| Cybersecurity Exposure | The vast attack surface of IoT devices and distributed networks, coupled with sophisticated AI-driven threats. | Non-negotiable security requirements, demanding proactive, predictive defense and Zero Trust adoption3. |
| Vendor Lock-in & Silos | Disparate vendor systems create data silos, hindering end-to-end visibility. | Costly, inflexible contracts and inability to optimize across the entire network4. |
| Sustainability Mandate | Massive energy consumption from 5G and data centers drives the need for a rapid transformation toward Net Zero. | Economic and regulatory pressure to integrate energy efficiency into network design. |
Reflections on 2025: From Potential to Practice
As I reflect on the entirety of 2025, it becomes evident that the year was marked not by a wave of groundbreaking inventions, but rather by the steady advancement and practical implementation of robust, established technologies. Over the past twelve months, the narrative shifted decisively from the anticipation of future possibilities to the tangible realisation of enterprise-ready solutions.
Across several critical sectors, we observed a transition: technologies that once held only theoretical promise are now being deployed at scale and integrated into real-world business operations. This maturation has underscored the value of reliable, effective tools, demonstrating how innovation is as much about refinement and application as it is about invention.
- Generative AI Democratizes Network Operations
If previous years were about the novelty of Generative AI, 2025 was about its utility. We moved beyond simple automation to true cognitive operations by integrating GenAI directly into the operational workflow.
- The Strategic Importance of Digital Twin Technology
The concept of a Digital Twin—a virtual replica of a physical system—is not new, but its application in telecom reached a critical maturity point in 2025. This technology allows MNOs to simulate complex changes, test new configurations, and predict the impact of traffic surges before they occur on the live network.
- Private 5G Powering Industry 4.0
The private network market accelerated rapidly, with projections showing a 65.4% CAGR in private 5G connections through 2030. Industries moved beyond proof-of-concept to live deployment, particularly in logistics and manufacturing.
- Cybersecurity as a Core Business Function
The increasing complexity of our networks and the rise of sophisticated AI-driven threats made cybersecurity a top priority in 2025. The focus shifted from reactive defense to proactive, predictive security postures. We saw greater adoption of Zero Trust architectures and AI-powered threat detection systems. For telecom operators, securing the vast attack surface of IoT devices and distributed networks became a non-negotiable aspect of service delivery.
- 5G Expansion and the Dawn of 6G Research
Throughout 2025, 5G continued its global expansion, particularly in emerging markets where its impact on enterprise connectivity is most profound. 6G research also increased exponentially in 2025 targeting specific applications like CF-MIMO , RIS and ISAC .
- Field Testing Takes to the Skies (Green Operations)
2025 marked a turning point for field testing sustainability. Traditional drive testing, with its high fuel consumption and limited access to difficult terrains, began to give way to drone-based solutions.
- AI-Automated Planning & The 15-Minute Optimization
The era of manual network planning effectively ended in 2025. The complexity of multi-layer networks made manual parameter tuning obsolete, we also perceived massive increase in the demand for SMART CAPEX and OPEX solutions.
- Active Probing & Service Assurance
As networks became more complex, “passive” monitoring was no longer enough. 2025 saw a rise in Active Service Assurance.
- Quantum Computing’s Cautious Breakthroughs
While still in its early stages, quantum computing made tangible progress in 2025. We saw advancements in qubit stability and error correction, moving quantum systems closer to solving real-world optimization problems that are intractable for classical computers. For telecom, this holds immense promise for complex tasks like network routing optimization and spectrum management. Though widespread application remains on the horizon, the progress this year has solidified its potential as a game-changing technology.
2026 Technological Outlook and Predictions

As the telecommunications industry builds upon the momentum generated in 2025, the year ahead is set to deliver significant advances in network intelligence and integration. The following are detailed forecasts for the principal trends that are expected to shape 2026:
- AI-Native Networks Become the Industry Standard
The application of artificial intelligence will evolve beyond mere overlays. In 2026, the emergence of AI-native networks will see machine learning deeply embedded within the air interface and protocol stack. Key network elements, such as Radio Units and Distributed Units, will develop “Sense-Think-Act” capabilities, empowering them to make micro-adjustments in beamforming and spectrum allocation within milliseconds.
- The Dark NOC as a Strategic Priority
In response to ongoing budgetary pressures, the Dark NOC—where up to 80% of operational tasks are autonomously managed—will become a primary strategic objective for mobile network operators (MNOs). This shift will redefine the role of human engineers, transitioning their focus from routine monitoring and repairs to governance and design. The reliance on vendor-agnostic platforms will increase, aiding in the unification of data across fragmented ecosystems.
- Transition to Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC)
The migration towards Post-Quantum Cryptography will progress from the planning stages to phased execution. Telecom operators are anticipated to begin upgrading encryption keys and hardware security modules, aiming to counteract the risk posed by potential adversaries who may harvest encrypted data now, with the intention of decrypting it in the future as quantum computing matures.
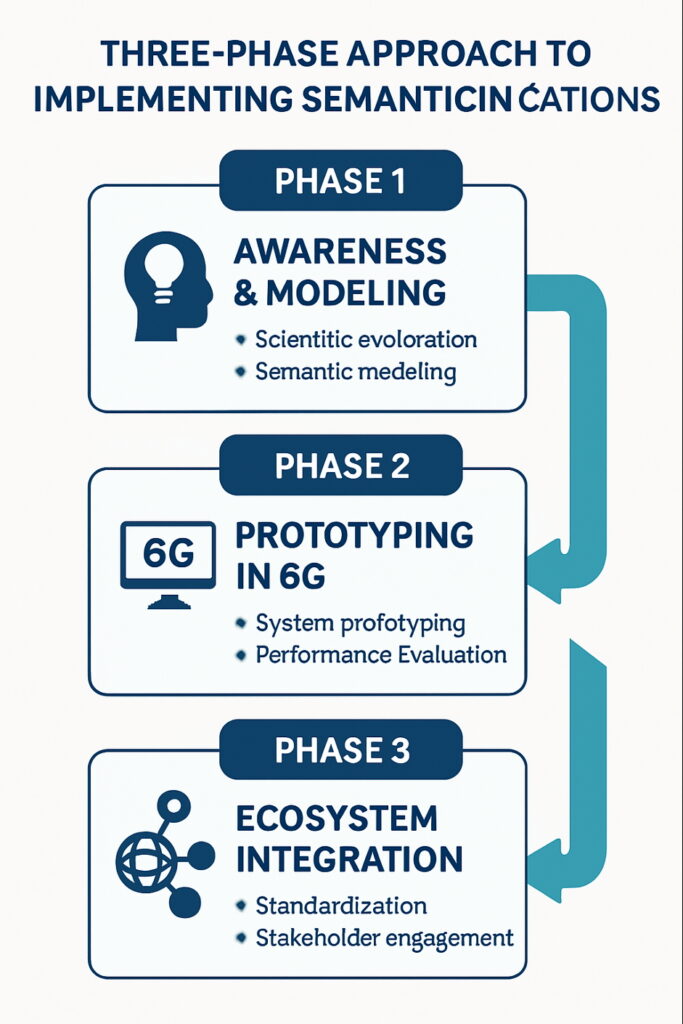
- Intensification of 6G Standards Prototyping
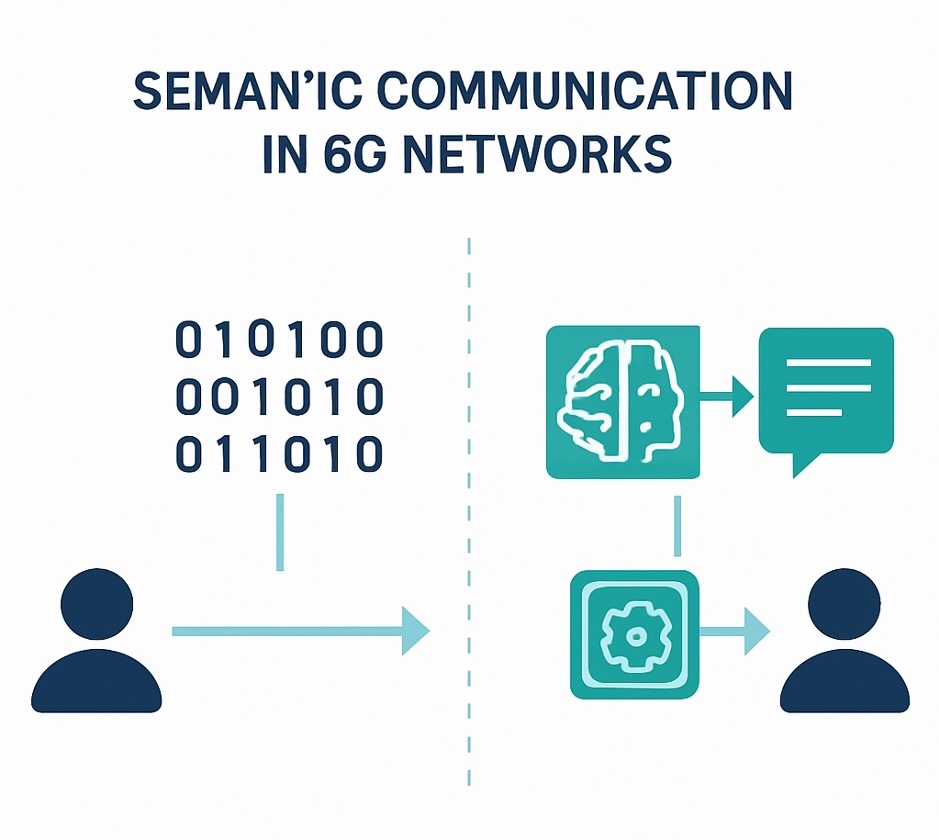
The development of 6G standards will move from theoretical discussions to tackling targeted engineering challenges. One of the central focuses will be Semantic Communications, which shifts the paradigm from transmitting raw bits to communicating actual meaning. By leveraging AI to filter out irrelevant data at the source, 6G networks are expected to realise substantial efficiency gains.
- Agentic AI and the Advancement of Cybersecurity Autonomy
2026 is poised to be recognised as the “Year of the Defender” due to the emergence of Agentic AI—autonomous systems capable of independent decision-making. These intelligent agents will prove indispensable in defending against AI-driven identity attacks. Unlike conventional static playbooks, Agentic AI can reason, adapt, and autonomously develop defence strategies to address vulnerabilities in real-time.
- Private Networks Will Drive Enterprise Digitalization
The demand for private networks will accelerate in 2026 as more enterprises recognize their value in achieving secure and reliable connectivity for mission-critical operations.
2025: A Year of Achievement

Throughout 2025, we played a pivotal role in driving technological advancements for our clients and customers. Acting as a cornerstone of progress, our team delivered a series of significant accomplishments that underscored our commitment to innovation and excellence. The following is a sample of the achievements realised during the year, reflecting our ongoing dedication to supporting our clients’ evolving needs and enabling their success in an increasingly complex technological landscape.
- Our KATANA platform proved essential here, offering a vendor-agnostic “Single Pane of Glass.” By integrating data from Huawei, Nokia, Ericsson, and new Open RAN vendors into one topology view, we solved the fragmentation issue. This enabled Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP) via our iMaster module, allowing devices to be automatically configured and integrated upon connection, regardless of the hardware vendor.
- We introduced ConnectSphere, an extension of our testing capabilities that deploys static probes in VIP areas and strategic locations. Unlike traditional drive tests that are periodic, these probes run 24/7 service testing to assure quality in real-time. This allows for proactive fault detection in both the Core and Radio domains, ensuring that high-value enterprise clients receive the Quality of Service (QoS) they demand
- We doubled down on OctoMind, our AI-based planning platform. By leveraging modules like X-Planner (for PCI/RSI planning) and ACP (Automatic Cell Planning), we moved from manual processes that took days to AI-driven optimization that takes just 15 minutes. This automation improved network performance metrics from 68% to 94% while eliminating human error in parameter configuration.
- We saw a surge in specialized use cases where Wi-Fi was insufficient. For instance, in pharmaceutical warehouses, we deployed Private 5G to support mission-critical forklift automation, autonomous mobile robots (AMR), and collision avoidance systems that require ultra-low latency. By implementing Managed Services that include L1 maintenance and radio optimization, we ensured these networks met stringent SLAs for reliability and security, keeping data strictly on-premises
- Through our INOS Air solution (in collaboration with DJI Enterprise), we enabled operators to conduct 5G, 4G, and 3G testing at specific altitudes (5m to 20m). This allows for testing in recreational areas, dense industrial compounds, and over water (marinas and ports) where cars simply cannot go. This shift not only expanded accessibility but also slashed OPEX and carbon footprints, aligning perfectly with the industry’s Net Zero goals by utilizing electric drones instead of fuel-heavy vehicles.
- We introduced GenAI Chatbots within our KATANA platform to democratize data access. Engineers no longer need complex SQL skills; they can simply ask natural language questions like “Which sites have hardware faults right now?” or “Why is the throughput low in site X?” to get instant, actionable insights. This capability allows non-technical staff to create business intelligence reports and resolve performance issues faster, significantly reducing the barrier to entry for advanced network analysis.
- We are actively leveraging and integrating Digital Twin technology into our cognitive solutions. By integrating the Digital Twin with the Network Data, we provide MNOs with a powerful tool for predictive Coverage and Capacity. This capability is a game-changer for planning and optimization, allowing MNOs to move from simply reacting to network events to proactively optimizing their infrastructure, ensuring network slicing integrity, and managing resources with unprecedented foresight.
Digis Squared Focus in the Next Chapter
Our strategic focus for the coming year is clear: to leverage our cognitive solutions to solve the industry’s most pressing challenges.
Private 5G: Cognitive Operations at the Edge
The successful deployment of Private 5G will hinge on the ability to deliver cognitive operations at the edge. Our focus will be on ensuring the success of these mission-critical networks by providing the necessary tools to manage unique demands. Tools like KATANA and ConnectSphere will be vital for ensuring real-time fault isolation, predictive capacity planning, and dynamic resource allocation for industrial automation.
Net Zero: Energy Efficiency as a Strategic Priority
The transformation toward Net Zero is a strategic priority. We will continue to refine our AI and cognitive tools to optimize network elements, dynamically power down resources based on predictive traffic patterns, and ensure that energy efficiency is a core design principle.
- Example: Our cognitive engine can predict low-traffic periods 72 hours in advance to automatically place specific 5G-enabled sites into an ultra-low power state, maximizing OPEX savings.
Expanding the Cognitive Toolkit
We will continue to expand the capabilities of our core platforms, further integrating the predictive power of the Digital Twin with the real-time insights of KATANA and the customer-centric metrics of INOS. Our goal is to provide a unified, vendor-agnostic platform that allows MNOs to achieve true operational autonomy and move confidently toward the Dark NOC.
Closure
The path forward is clear: the only way to manage the complexity, cost, and security demands of modern telecom networks is through intelligence. For telecom operators in emerging markets, these advancements offer a chance to leapfrog legacy systems and build agile, efficient, and intelligent networks.
At Digis Squared, we are committed to turning these technological possibilities into operational realities for our partners. By focusing on cognitive operations powered by KATANA, INOS, OctoMind, and Digital Twin technology, we are not just optimizing networks; we are building the future of telecommunications—a future that is more efficient, more secure, and more sustainable.
Author: Abdelrahman Fady | CTO | Digis Squared