Technology sunset & spectrum refarming | Navigating a path from legacy technologies to the future.
Amr Maged, Co-Founder & Chief Strategy Officer at Digis Squared, considers the benefits and issues of refarming spectrum, and the scope and timelines of such projects. This blog post follows on from CTO Abdelrahman’s previous Technology Sunset blog, and was first published here as a downloadable short, graphic-rich document on LinkedIn.
The background
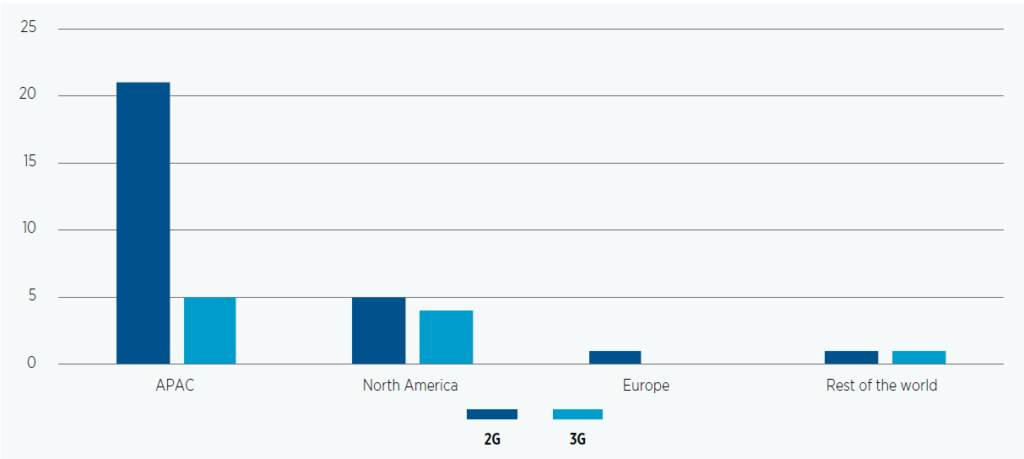
As 5G rollouts gather pace globally, and new technology deployments continue their unstoppable march, many networks are also grappling with what to do about legacy technologies. In 1991 Radiolinja launched 2G in Finland, and 2001 brought the first 3G launch, achieved by NTT DoCoMo in Japan – both network technologies are still in active commercial use around the world, but for how much longer? Technology sunset strategies consider how to re-allocate and optimise finite spectrum resources, efficiently, whilst taking care of customer impact.
Pro’s & con’s of re-farming 2G and or 3G spectrum
2G & 3G (Keep one of them, but arguments apply to both)
Why keep it?
- When VoLTE not available, voice calls fall back to 2G or 3G network (CSFB, circuit-switched fall back).
- Calls from a VoLTE handset to a 2G/3G handset use CSFB over 2G /3G.
- Early implementations of eCall service in Europe use 2G/3G for the voice call element of the mandatory service – no plans were made to be able to replace the equipment in these vehicles.
- Most IoT devices don’t need the high bandwidth 4G and 5G deliver, and can make service cost-prohibitive.
Why switch it off?
- Re-allocate spectrum: new 4G and 5G technologies are more efficient and more capable, delivering enhanced speed, bandwidth and security.
- Operational cost optimisation.
- IoT: LPWA-LTE, NB-IoT and other new technologies maximise battery life and battery cost, data usage, indoor coverage, and have lower cost modules.
- Regulatory driven spectrum reallocation and or harmonisation.
2G
Why keep it?
- 3G devices can “roll down” to 2G connectivity.
- Support 2G-only consumer handsets –typically low income, or elderly seeking simpler devices.
- Support 2G-only M2M devices
- Early M2M devices in tricky to reach geographies, or deep within long-life equipment (cars) and never designed for replacement.
- Early implementations of eCall service in Europe (uses 2G/3G for the voice call element of the mandatory service.)
- IoT devices deep inside buildings (indoor coverage).
- 2G base stations can be installed further apart – robust voice services over a large territory, more efficiently than 3G.
- Smaller carrier bandwidth spare, enables more bandwidth for 4G and 5G.
Why switch it off?
- Generally, lower number of 2G-only users than 3G, and lower ARPU.
- 2G delivers lower spectral efficiency than 3G.
- 2G voice calls are lower quality than 3G.
- Very limited data services in areas with no 4G coverage.
3G
Why keep it?
- Some MNOs: 3G network costs not yet amortised.
- 3G & HSPA provide far better data experience than 2G.
- Multi-RAB concept gives 3G users the option of having both voice and data services simultaneously.
- Performance of 3G interoperability with 4G + 5G is far better than 2G interoperability with 4G + 5G.
Why switch it off?
- 3G devices can “roll down” to 2G connectivity.
- Re-use 3G spectrum to add more capacity to LTE networks + expand 5G networks.
- 3G is not operating in band 3 (1800 MHZ band), the most famous 4G band – this is a significant limitation from the point of view of technology combination.
Technology sunset timeline
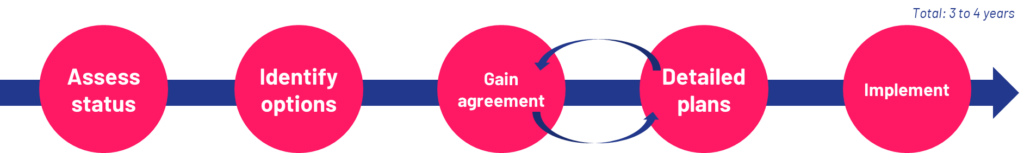
Whilst all projects vary, this indicative timeline highlights key milestones on the path from legacy technologies to the future.
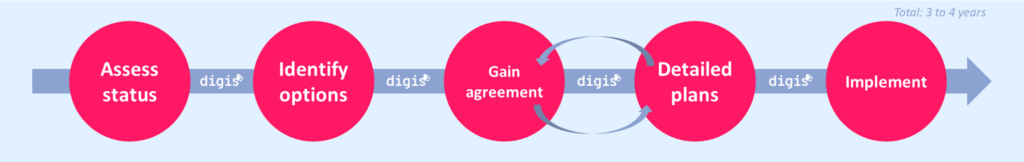
1. Assess status
- License end dates and regulatory requirements
- Assess spectrum availability
- Re-farm existing spectrum
- Options/ timeline to acquire
- Government expectations around new technology deployment
- Competitor activity & plans
- Infrastructure contract status incl backhaul, transmission and towers
- Subscriber network stats and forecasts (incl roaming and coverage)
- Other market constraints (MVNO contracts, M2M installed base and limitations….)
- Assess the RRUs & BBUs used, and their current configuration
2. Identify options
- Agree governance and scope
- Migration impacts, risks and mitigations, including,
- Coverage and infrastructure forecasts
- Brand perception
- Contracts: new and revised infrastructure and support contracts, extra fibre backbone services, additional project resource, lower energy consumption
- Savings delivered and investments needed
- Roaming contracts
- Timescale: lights out on one day, or slower decommissioning cells and degrading network over 6 months to 2 years?
3. Gain agreement
- Telecom Regulatory approval needed? Co-ordinated sunset activity and communication across sector? Is a shared legacy network required?
- M2M: complex customer migration plans (may involve Energy Regulator), consider how to recognise costs
- Elderly groups: address concerns and sell simple handsets
- Board sign-off
4. Detailed plans
- Date to stop selling new 2G / 3G subscriptions
- Consumer: campaign to churn and recycle legacy handsets, maintain affordable and simple option
- Extend coverage address gaps
- Work with M2M partners and customers (many are international, and may have experience in other territories)
- IoT /all contracts: ensure provision for future technology sunsets
- Procurement & legal contracts
- Training: ops, retail and customer-facing staff
- Return to 3, and repeat as needed
5. Implement
- Maintain quality of service and extend coverage, handle increased data demand, and continue to optimise networks as balance changes
- IoT: don’t underestimate complexity + some old implementations may be undocumented
- Learn lessons: will need to switch off other networks in future
Discover more
This blog post is also available as a stand-alone white paper.
Amr Maged, Co-Founder & Chief Strategy Officer at Digis Squared.
Please get in touch: use this link or email sales@DigisSquared.com .
Keep up to speed with company updates, product launches and our quarterly newsletter, sign up here.
Digis Squared, independent telecoms expertise.
Sources
- The Mobile Economy 2020, GSMA / GSMA Mobile Intelligence, Q1 2020
- Mobility Report, Ericsson, June 2020
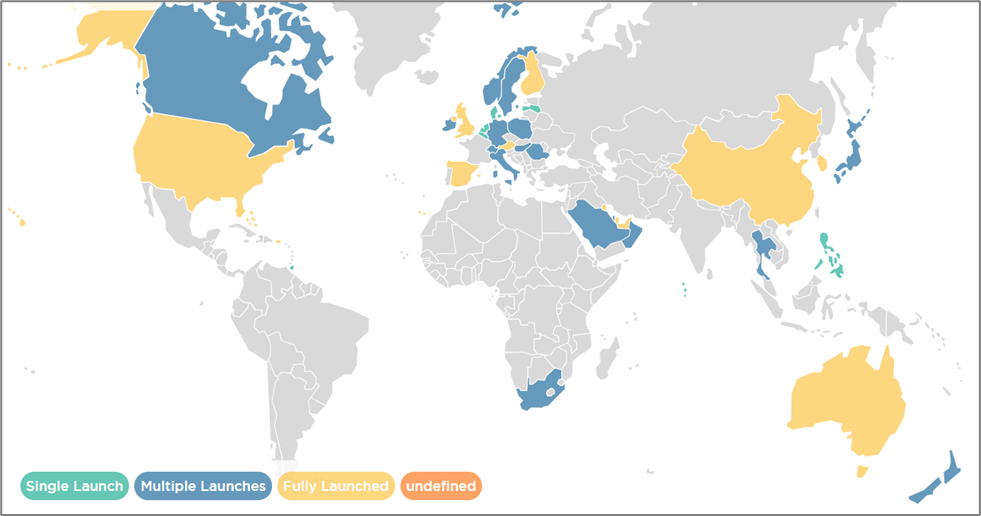
- Legacy mobile network rationalisation, experiences of 2G and 3G migrations in Asia-Pacific, GSMA, May 2020
Abbreviations
- ARPU: Average Revenue Per User
- BBU: Baseband Unit
- CAT-M1: see LTE-M.
- CSFB: Circuit Switched Fallback
- NB-IoT: Narrowband Internet of Things. One of two data networking technologies available on 4G (the other is LTE-M, aka CAT-M1). Intended for narrow band (250 kbps) low power data applications and does not support voice communications.
- LTE-M: LTE Machine Type Communication. Also known as Cat-M1. One of two data networking technologies available on 4G (the other is NB-IoT). Provides considerably higher bandwidth (1Mbps), supports voice and full mobility.
- RRU: Remote Radio Unit
- VoLTE: Voice over LTE
Image credits: Quino Al